CAR-T cell therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, illustration
Bildnummer 14247061
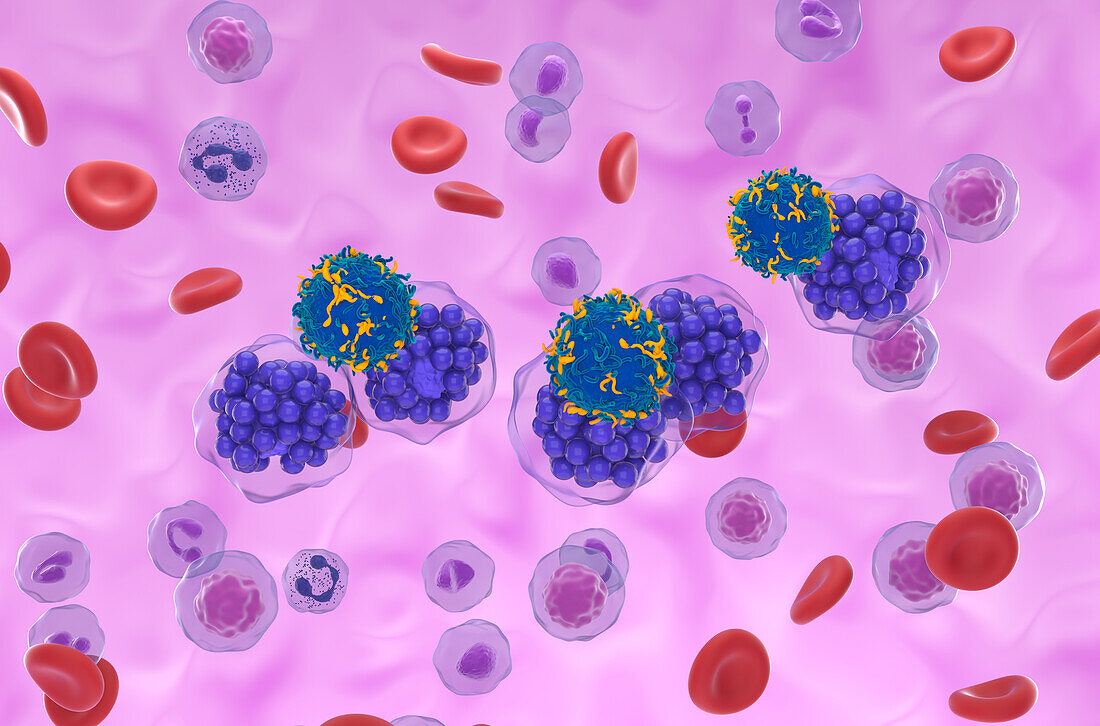
| Illustration showing chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells (blue) being used to treat diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells (purple). DLBCL is a common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, or cancer of the lymphatic system. It affects B lymphocytes, a white blood cell that produces antibodies to fight against infection. DLBCL normally develops in the lymph nodes causing uncontrollable growth of the B lymphocytes. It is typically fast-growing, and requires combined chemotherapy and immunotherapy. CAR-T therapy is a type of immunotherapy that genetically modifies a patient's own T cells, another form of white blood cell, to recognise and destroy cancer cells. | |
| Lizenzart: | Lizenzfrei |
| Credit: | Science Photo Library / NEMES LASZLO |
| Modell-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Eigentums-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Restrictions: | - |
Preise für dieses Bild ab 29 €
Für digitale Nutzung (72 dpi)
ab 29 €
Für Druckauflösung (300 dpi)
ab 300 €
Keywords
- 3D,
- abnormal,
- Antikörper,
- Auto,
- Behandlung,
- Biologie,
- biologisch,
- Blut,
- Blutgefäß,
- Blutzellen,
- cgi,
- Dreidimensional,
- genetisch verändert,
- Hämatologie,
- hämatologisch,
- Illustration,
- Immunologie,
- immunologisch,
- Kondition,
- Krankheit,
- Krebs,
- krebsartig,
- Kunstwerk,
- Lymphknoten,
- Lymphom,
- Lymphozyten,
- Lymphsystem,
- maligne,
- Malignom,
- Medizin,
- medizinisch,
- menschlicher Körper,
- Niemand,
- Onkologie,
- onkologisch,
- Rosa Hintergrund,
- rote Blutkörperchen,
- Störung,
- Struktur,
- strukturell,
- therapeutisch,
- Therapie,
- Tumor,
- ungesund,
- weiße Blutkörperchen,
- weißes Blutkörperchen,
- Zelle,
- Zellen
