White blood cells responding to bacterial infection, illustration
Bildnummer 14233463
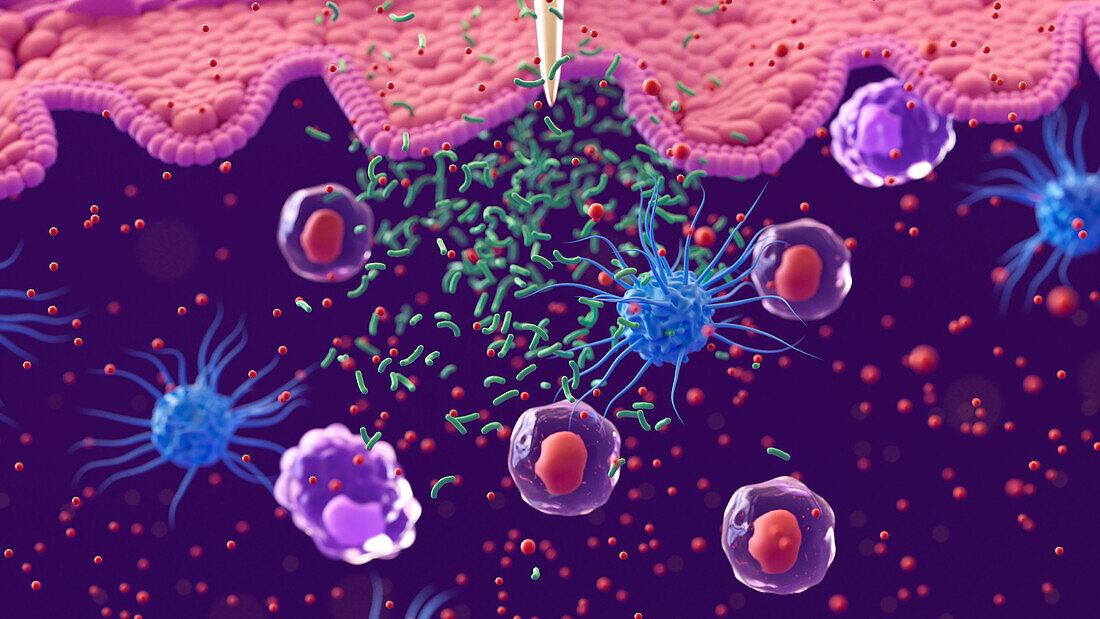
| Illustration showing white blood cells responding to bacteria (green) entering the body through a breach in the skin's outer layer (epidermis, pink) caused by a needle (top centre). Three types of white blood cell are present: dendritic cells (blue), T helper cells (Th cells, red nuclei) and macrophages (purple). White blood cells cells recognise substances that should not be present in a healthy human body and help to nullify them. The dendritic and Th cells are releasing cytokines (orange dots), small signalling proteins, in response to the bacteria. Cytokines are important in attracting more white blood cells once an infection has been found and coordinating the immune response. Macrophages are specialised for engulfing and destroying substances that have triggered an immune response. | |
| Lizenzart: | Lizenzfrei |
| Credit: | Science Photo Library / DESIGN CELLS |
| Modell-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Eigentums-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Restrictions: | - |
Preise für dieses Bild ab 29 €
Für digitale Nutzung (72 dpi)
ab 29 €
Für Druckauflösung (300 dpi)
ab 300 €
Keywords
- 3D,
- Bakterien,
- Bakteriologie,
- bakteriologisch,
- Bakterium,
- Biologie,
- biologisch,
- Blauer Hintergrund,
- Blutzelle,
- Dreidimensional,
- entzündlich,
- Entzündung,
- Epidermis,
- Haut,
- Illustration,
- Immunologie,
- immunologisch,
- Immunreaktion,
- Immunsystem,
- Immunzelle,
- Infektion,
- Kunstwerk,
- Leukozyt,
- Leukozyten,
- Nadel,
- Niemand,
- Phagozyten,
- Proteine,
- Verletzung,
- weißes Blutkörperchen,
- Wunde,
- Zelle
