Cytomegalovirus, TEM
Bildnummer 14167769
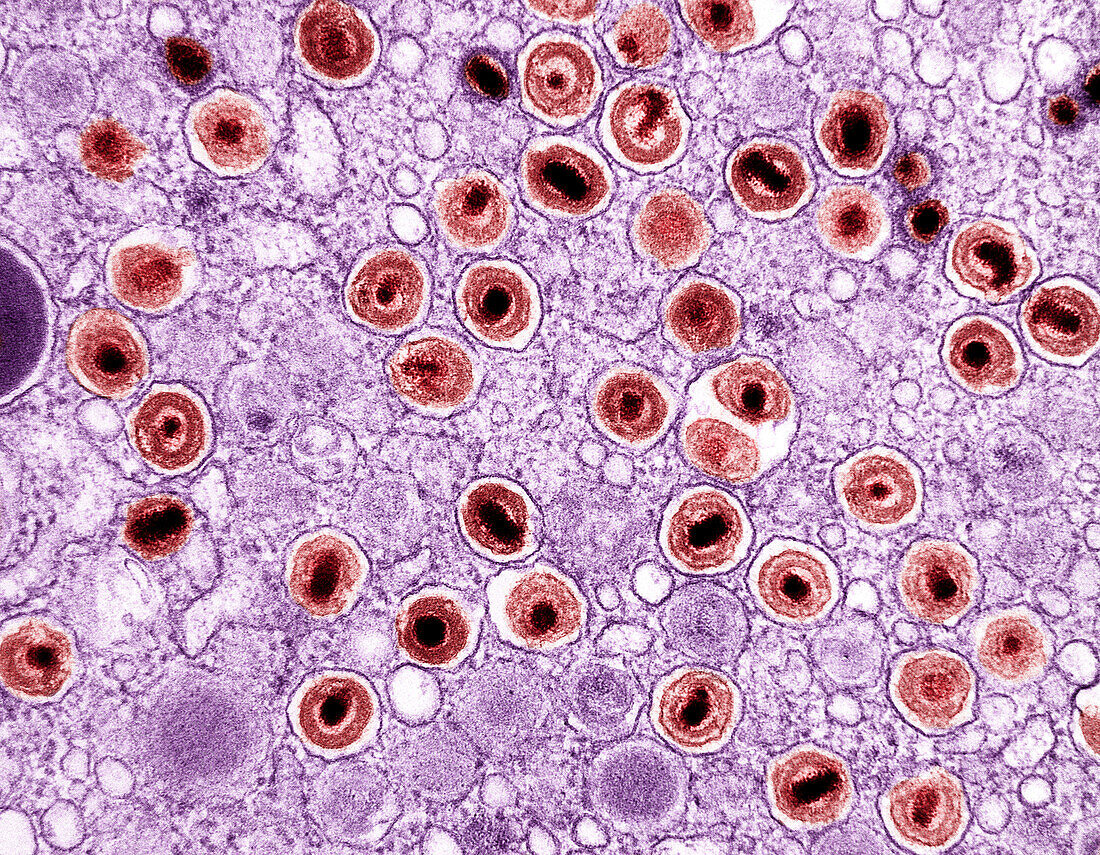
| Coloured transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of cytomegalovirus (CMV) particles (red) in intracellular vesicles in an infected macrophage (immune cell, pink). Cytomegaloviruses are a genus of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses which infect humans and monkeys. CMV infection is a common chronic infection affecting people of all ages. It is symptomless in most cases, but can cause flu-like symptoms upon initial infection. It can be passed to babies before birth (congenital CMV), in which case more serious symptoms can occur, including a rash, yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice), low birth weight, a smaller head than usual (microcephaly), seizures and problems with the eyes, ears, liver and spleen. CMV typically self-resolves, though antivirals are sometimes used to treat babies. | |
| Lizenzart: | Lizenzpflichtig |
| Credit: | Science Photo Library / NIAID |
| Bildgröße: | 3560 px × 2768 px |
| Modell-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Eigentums-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Restrictions: | - |
Preise für dieses Bild ab 15 €
Universitäten & Organisationen
(Informationsmaterial Digital, Informationsmaterial Print, Lehrmaterial Digital etc.)
ab 15 €
Redaktionell
(Bücher, Bücher: Sach- und Fachliteratur, Digitale Medien (redaktionell) etc.)
ab 30 €
Werbung
(Anzeigen, Aussenwerbung, Digitale Medien, Fernsehwerbung, Karten, Werbemittel, Zeitschriften etc.)
ab 55 €
Handelsprodukte
(bedruckte Textilie, Kalender, Postkarte, Grußkarte, Verpackung etc.)
ab 75 €
Pauschalpreise
Rechtepakete für die unbeschränkte Bildnutzung in Print oder Online
ab 495 €
Keywords
- abnormal,
- Biologie,
- biologisch,
- CMV,
- Cytomegalovirus,
- DNA-Virus,
- eingefärbt,
- Epidemiologie,
- Erreger,
- Farbig,
- Gewebe,
- Histopathologie,
- histopathologisch,
- Immunzelle,
- Infektion,
- infiziert,
- Makrophagen,
- Mikrobiologie,
- mikrobiologisch,
- Mikrofotografie,
- Niemand,
- pathogen,
- Rosa Hintergrund,
- tem,
- Transmissionselektronenmikroskopie,
- transmissionselektronenmikroskopische Aufnahme,
- ungesund,
- viral,
- Virion,
- Virologie,
- virologisch,
- Virus,
- Viruspartikel,
- weißes Blutkörperchen,
- weißes Blutkörperchen,
- Zelle,
- zellular
