Gamma ray scan of healthy human kidneys
Bildnummer 12496943
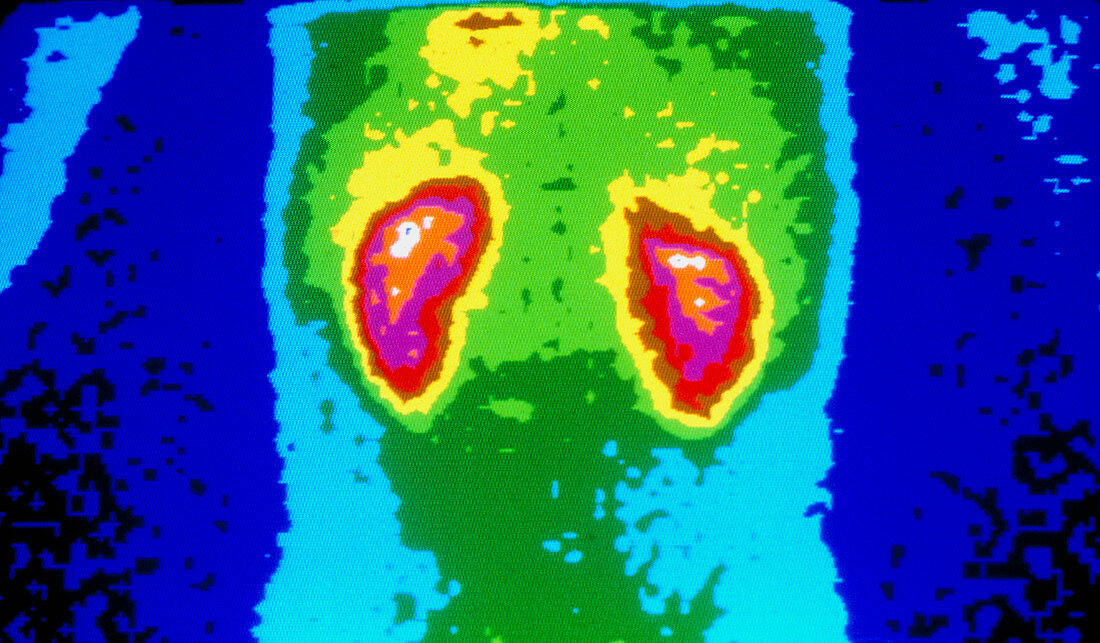
| Human kidneys. Coloured gamma scan (scintigram) of healthy human kidneys, which excrete urine and regulate the blood and electrolyte balance. The kidneys' centres (orange/white) have absorbed more radioactive tracer than their outsides (yellow/ brown). Gamma scanning involves introducing a radioactive isotope (radionuclide) into the body, in this case Technetium-99m, which accumulates in the target organ. The isotope emits gamma rays which are detected as flashes of light by a gamma camera. Isotopes are chosen for their ability to gather in cancerous or inflamed tissue, producing 'hot spots'. Gamma scans are tissue slices""." | |
| Lizenzart: | Lizenzpflichtig |
| Credit: | Science Photo Library / PROF. J. LEVEILLE |
| Bildgröße: | 4245 px × 2480 px |
| Modell-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Eigentums-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Restrictions: | - |
Preise für dieses Bild ab 15 €
Universitäten & Organisationen
(Informationsmaterial Digital, Informationsmaterial Print, Lehrmaterial Digital etc.)
ab 15 €
Redaktionell
(Bücher, Bücher: Sach- und Fachliteratur, Digitale Medien (redaktionell) etc.)
ab 30 €
Werbung
(Anzeigen, Aussenwerbung, Digitale Medien, Fernsehwerbung, Karten, Werbemittel, Zeitschriften etc.)
ab 55 €
Handelsprodukte
(bedruckte Textilie, Kalender, Postkarte, Grußkarte, Verpackung etc.)
ab 75 €
Pauschalpreise
Rechtepakete für die unbeschränkte Bildnutzung in Print oder Online
ab 495 €
