Red blood cell in a tiny capillary, TEM
Bildnummer 12298259
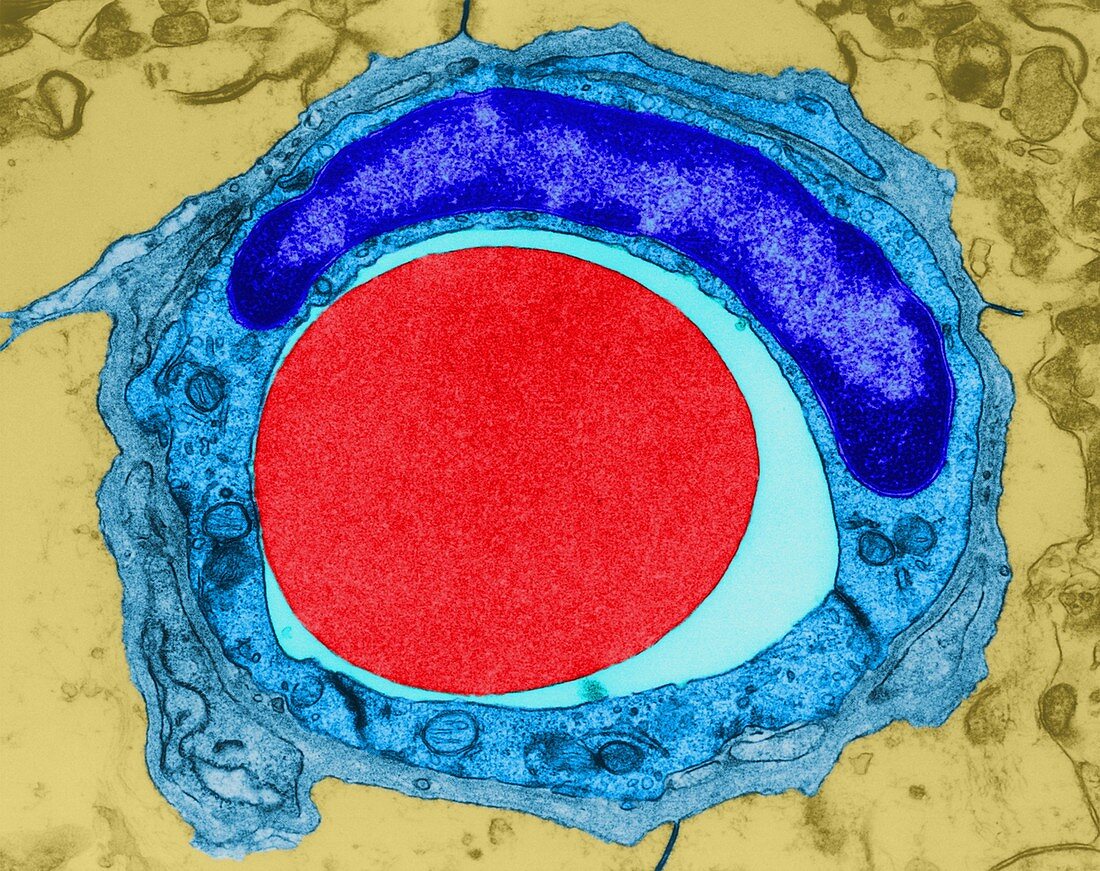
| Red blood cell in a tiny capillary (human central nervous system), coloured transmission electron micrograph (TEM). Note the endothelial cell (containing a large nucleus) that forms the capillary. Red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, are the most common type of blood cell in vertebrates. They are involved in delivering oxygen to the body tissue. The cytoplasm of RBCs is rich in haemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids and this structure provides properties essential for physiological cell function (deformability and stability) while traversing the circulatory system, especially the capillary network. In humans, mature RBCs are flexible and oval biconcave disks. Capillaries are the small blood vessels that make up the microcirculation of the human body. Magnification: x5, 370 when shortest axis printed at 25 | |
| Lizenzart: | Lizenzpflichtig |
| Credit: | Science Photo Library / DENNIS KUNKEL MICROSCOPY |
| Bildgröße: | 3321 px × 2631 px |
| Modell-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Eigentums-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Restrictions: | - |
Preise für dieses Bild ab 15 €
Universitäten & Organisationen
(Informationsmaterial Digital, Informationsmaterial Print, Lehrmaterial Digital etc.)
ab 15 €
Redaktionell
(Bücher, Bücher: Sach- und Fachliteratur, Digitale Medien (redaktionell) etc.)
ab 30 €
Werbung
(Anzeigen, Aussenwerbung, Digitale Medien, Fernsehwerbung, Karten, Werbemittel, Zeitschriften etc.)
ab 55 €
Handelsprodukte
(bedruckte Textilie, Kalender, Postkarte, Grußkarte, Verpackung etc.)
ab 75 €
Pauschalpreise
Rechtepakete für die unbeschränkte Bildnutzung in Print oder Online
ab 495 €
