Mitosis,Metaphase,TEM
Bildnummer 12047158
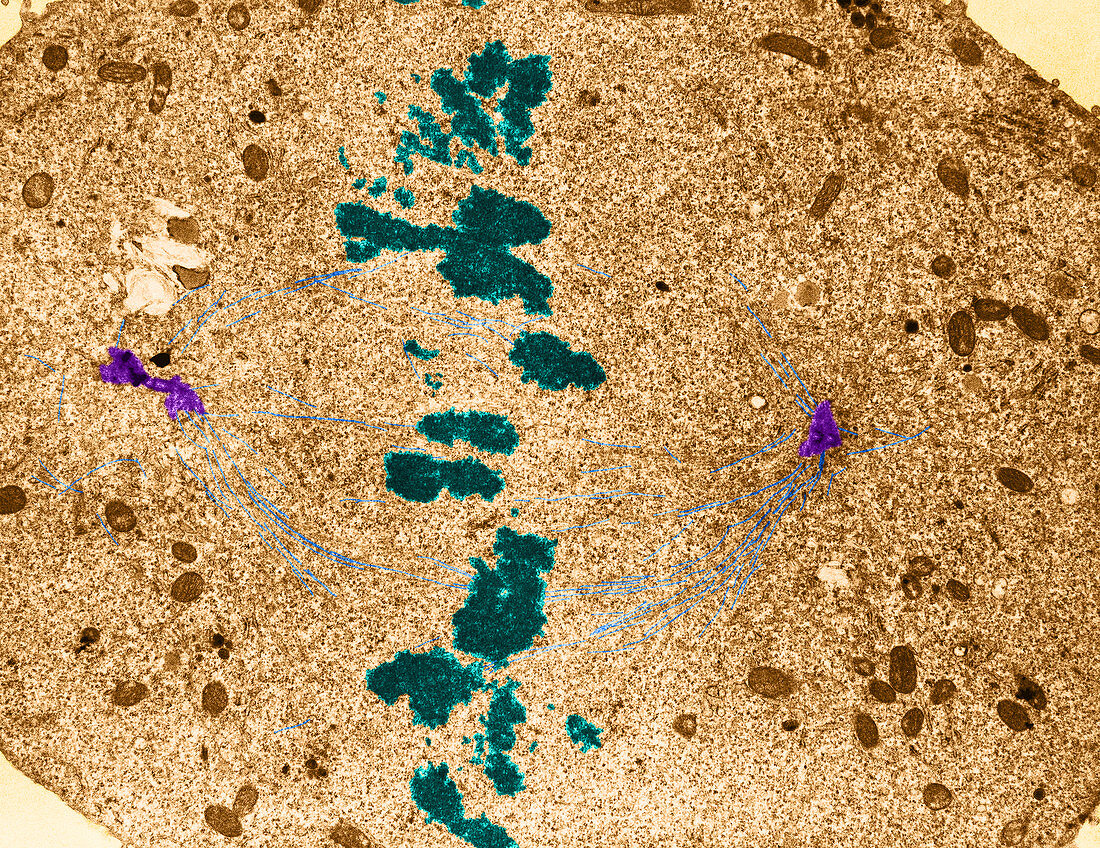
| Colour enhanced transmission electron micrograph showing mitosis - metaphase,note the centrioles (purple). Human placenta. No magnification given. Mitosis,the usual method of cell division,characterized typically by the resolving of the chromatin of the nucleus into a threadlike form,which condenses into chromosomes,each of which separates longitudinally into two parts,one part of each chromosome being retained in each of two new cells resulting from the original cell. The four main phases of mitosis are prophase,metaphase,anaphase,and telophase. A centriole is a small,cylindrical cell organelle,seen near the nucleus in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotic cells,that divides in perpendicular fashion during mitosis,the new pair of centrioles moving ahead of the spindle to opposite poles of the cell as the cell divides: identical in internal structure to a basal body | |
| Lizenzart: | Lizenzpflichtig |
| Credit: | Science Photo Library / Phillips, David M. |
| Bildgröße: | 4761 px × 3671 px |
| Modell-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Eigentums-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Restrictions: |
|
Preise für dieses Bild ab 15 €
Universitäten & Organisationen
(Informationsmaterial Digital, Informationsmaterial Print, Lehrmaterial Digital etc.)
ab 15 €
Redaktionell
(Bücher, Bücher: Sach- und Fachliteratur, Digitale Medien (redaktionell) etc.)
ab 30 €
Werbung
(Anzeigen, Aussenwerbung, Digitale Medien, Fernsehwerbung, Karten, Werbemittel, Zeitschriften etc.)
ab 55 €
Handelsprodukte
(bedruckte Textilie, Kalender, Postkarte, Grußkarte, Verpackung etc.)
ab 75 €
Pauschalpreise
Rechtepakete für die unbeschränkte Bildnutzung in Print oder Online
ab 495 €
Keywords
- Biologie,
- eingefärbt,
- elektronenmikroskopische Aufnahme,
- em,
- Eukaryot,
- Histologie,
- Mensch,
- Mikrofotografie,
- Mikrographie,
- Mikroskopie,
- mikroskopisch,
- Mitose,
- Niemand,
- Organelle,
- Physiologie,
- Reproduktion,
- Säugetier-,
- tem,
- Transmissionselektronen,
- verbessert,
- Zelle,
- Zellstruktur,
- zellular,
- Zytologie,
- Zytoplasma
