West Nile Virus
Bildnummer 12029472
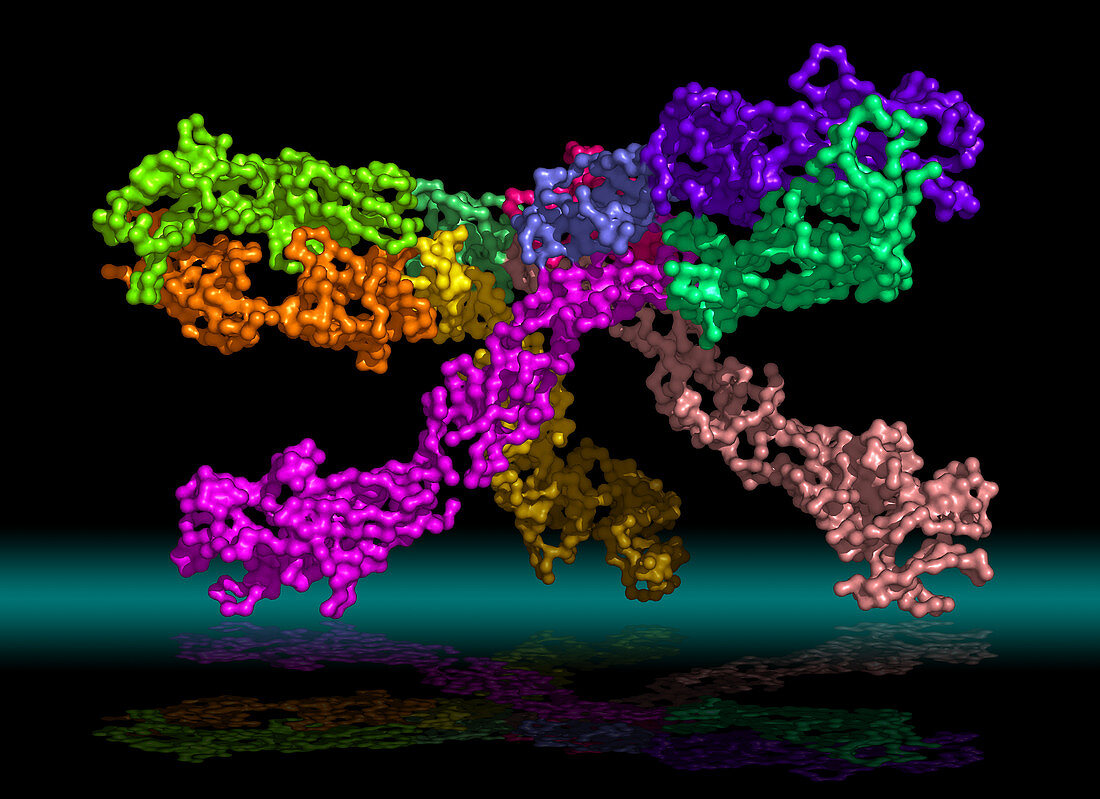
| Flaviviruses are a group of human pathogens causing severe encephalitic or haemorrhagic diseases that include West Nile,dengue and yellow fever viruses. Here,using X-ray crystallography we have defined the structure of the flavivirus cross-reactive antibody E53 that engages the highly conserved fusion loop of the West Nile virus envelope glycoprotein. Using cryo-electron microscopy,we also determined that E53 Fab binds preferentially to spikes in noninfectious,immature flavivirions but is unable to bind significantly to mature virions,consistent with the limited solvent exposure of the epitope. We conclude that the neutralizing impact of E53 and likely similar fusion-loop-specific antibodies depends on its binding to the frequently observed immature | |
| Lizenzart: | Lizenzpflichtig |
| Credit: | Science Photo Library / Degginger, Phil |
| Bildgröße: | 9192 px × 6676 px |
| Modell-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Eigentums-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Restrictions: |
|
Preise für dieses Bild ab 15 €
Universitäten & Organisationen
(Informationsmaterial Digital, Informationsmaterial Print, Lehrmaterial Digital etc.)
ab 15 €
Redaktionell
(Bücher, Bücher: Sach- und Fachliteratur, Digitale Medien (redaktionell) etc.)
ab 30 €
Werbung
(Anzeigen, Aussenwerbung, Digitale Medien, Fernsehwerbung, Karten, Werbemittel, Zeitschriften etc.)
ab 55 €
Handelsprodukte
(bedruckte Textilie, Kalender, Postkarte, Grußkarte, Verpackung etc.)
ab 75 €
Pauschalpreise
Rechtepakete für die unbeschränkte Bildnutzung in Print oder Online
ab 495 €
