Electrical conduction of the heart
Bildnummer 11595724
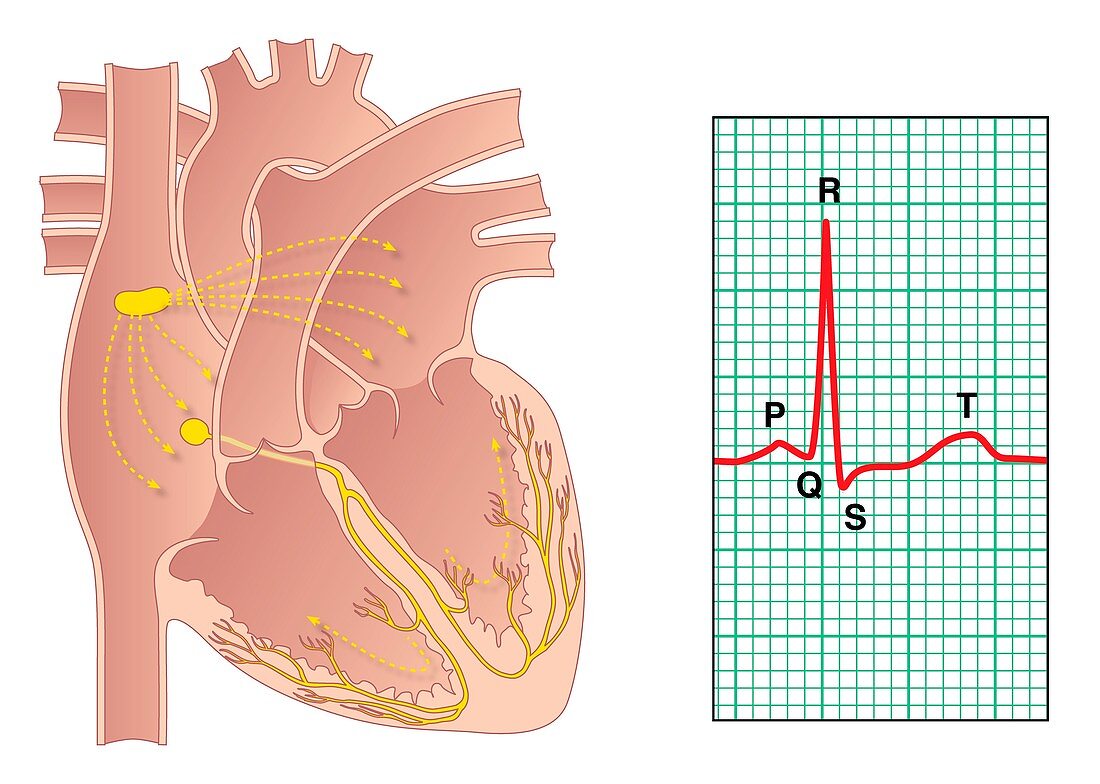
| Electrical conduction of the heart. Artwork showing the impulse conduction system (yellow) of the human heart (left) and an electrocardiogram (ECG) of a normal heart rate (right). The sinoatrial (SA) node (yellow,upper left) consists of self-excitatory muscle cells that contract rhythmically at around 70 beats per minute. Following each contraction,an impulse spreads through the heart's upper chambers (atria,upper frame) to the atrioventricular (AV) node (yellow,centre left). Contraction of the atria causes blood to move into the lower chambers (ventricles,lower frame). This contraction is seen as the P wave on the ECG. The AV node transmits the impulse to the ventricles,via the bundle of His. The ventricles contract,sending blood to the lungs and to the rest of the body. The ventricular contraction is seen as the QRS wave complex on the ECG. The T wave is the relaxation of the ventricles | |
| Lizenzart: | Lizenzpflichtig |
| Credit: | Science Photo Library / Gardiner, Peter |
| Bildgröße: | 4970 px × 3543 px |
| Modell-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Eigentums-Rechte: | nicht erforderlich |
| Restrictions: | - |
Preise für dieses Bild ab 15 €
Universitäten & Organisationen
(Informationsmaterial Digital, Informationsmaterial Print, Lehrmaterial Digital etc.)
ab 15 €
Redaktionell
(Bücher, Bücher: Sach- und Fachliteratur, Digitale Medien (redaktionell) etc.)
ab 30 €
Werbung
(Anzeigen, Aussenwerbung, Digitale Medien, Fernsehwerbung, Karten, Werbemittel, Zeitschriften etc.)
ab 55 €
Handelsprodukte
(bedruckte Textilie, Kalender, Postkarte, Grußkarte, Verpackung etc.)
ab 75 €
Pauschalpreise
Rechtepakete für die unbeschränkte Bildnutzung in Print oder Online
ab 495 €
